#209 Of New Beginnings and Old Grouses
Another Bank Goes Down in the US, India's Transition Away from Coal Power, and Apple's India Turnaround
Global Policy Watch: Chronicle Of A Crisis Foretold
Reflections on global policy issues
— RSJ
A major state election (Karnataka) is coming up this week. But there’s hardly anything worth analysing. The Congress seemed to have a slight edge in the early opinion polls, but that’s wearing thin. The BJP, always with its ears to the ground, has cranked up its poll machinery in the last couple of weeks drawing upon the star power of the PM in the urban areas of the state. The friendly media houses have been mobilised to pick up ‘emotive’ issues that would tilt the scale in favour of the party in power. It is not too difficult to figure out what the average voter wants if you go by the opinion polls and surveys. But those substantive issues just don’t feature in the public discourse. If you read the papers or media reports on what’s being debated among parties in Karnataka, it is about who is a Hindu hater, who prostrates more often before deities and how going back to the OPS (old pension scheme) is such a wonderful idea. In the classical model of how representative democracy ought to work, the voters would have a limited view of how the world works, and it is the representative who owes the voters not only his labour but also his judgment on issues (to riff on Burke).
That seems to be inverted here. One set of representatives has, over the last few years, instituted all kinds of targeted laws - hijaab ban, anti-conversion laws, scrapping minority quotas and cow slaughter ban - in the hope that they will yield electoral gains. The other set is talking of another set of bans convenient to them and some really bad economic policies. We often say that this newsletter attempts to change the demand side of the political equation by making people more aware of public policies and demanding better from their representatives. What we have here is the public demanding the right kind of things (if opinion polls are to go by), but their representatives are keen on dragging them back to divisive emotive issues. The Karnataka election will be a good test of what prevails eventually. I can almost see the straight line from these polls to the general elections due almost exactly 12 months from now. We will all be debating similar trivial issues than what really should matter to India. For some reason, that doesn’t make for a good topic of debate. It makes any election analysis a waste of time, really.
Switching gears, as I finished writing my last week’s edition on what the US Fed refuses to learn from the SVB collapse, another mid-sized US bank, the First Republic Bank (FRB), went down and was sold to J.P. Morgan, the ultimate backstop in the US financial system. No amount of assurance from FDIC to the depositors of the bank nor the combined infusion of capital about a month back from a consortium of big banks into FRB was enough to stanch the outflow of deposits. Soon the bank was insolvent, the shareholders and bondholders lost everything, and J.P. Morgan was given enough of a sweet deal to pick up the pieces. I’m sure the Fed will come out with another report on the FRB collapse where it will blame the management for not hedging its treasury risks and being lax in its risk practices. There will be a light rap to the supervisors and staff from Fed who monitored FRB, and that will be that. I hope there’s some more introspection by the Fed than that. Because as the shares of PacWest and Western Alliance have sunk over the last two days, it is clear that a number of mid-sized banks are going to collapse in slow-motion and end up in the lap of J.P. Morgan or FDIC very soon. The feeble Fed response was a 25 bps hike in rates last week with a strong indication that it will hit the pause button on hikes now. The question is if that’s enough to structurally save many of these banks.
I have argued for the past couple of months (just after the SVB collapse) that there are three problems for the Fed to contend with, and there are no real answers for them. It is Hail Mary time. Choose the best among the worst options and brace for the impact. I will lay out the three problems it faces before suggesting what looks like the best of the worst option that the Fed has chosen.
First, the Fed continued raising interest rates to fight inflation without thinking through its impact on the banking system. This much is clear now. The surprises that have come up in the shape of SVB, Signature and FRB weren’t anticipated at all. As the interest rates rose, the value of the long-term assets held by banks has fallen while their liabilities, in the form of deposits, which tend to be shorter in term, haven’t fallen as much. The slowdown in the economy has meant there’s not enough demand for credit at elevated rates, which means banks continue to invest in long-term US treasury bills. Every time the rates go up, these held-to-maturity (HTM) assets take a notional mark-to-market loss. A recent report by the Hoover Institution suggests that at this moment, the US Banking system’s market value of assets is about $ 2 trillion below their book value. In an article on Yahoo Finance, Ambrose Evan-Pritchards writes:
The second and third biggest bank failures in US history have followed in quick succession. The US Treasury and Federal Reserve would like us to believe that they are “idiosyncratic”. That is a dangerous evasion.
Almost half of America’s 4,800 banks are already burning through their capital buffers. They may not have to mark all losses to market under US accounting rules but that does not make them solvent. Somebody will take those losses.
“It’s spooky. Thousands of banks are underwater,” said Professor Amit Seru, a banking expert at Stanford University. “Let’s not pretend that this is just about Silicon Valley Bank and First Republic. A lot of the US banking system is potentially insolvent.”
The second problem, which kind of starts giving this a contagion feel, is the state of the commercial property market in the US. Interest rates have moved up too fast, the slowdown is real with many large employers laying off people, so there’s no real need for commercial capacity, and the excess liquidity fuelled by the Fed during the pandemic meant additional capacity was built up cheaply, which now has no takers. What’s worse, the rapid increase in rates means that a lot of these loans that will come up for refinancing soon (at higher rates) will face defaults. The mid-sized regional banks have a sizable exposure to commercial real estate, with estimates that about two-thirds of all commercial property borrowing comes from them. From the same Yahoo Finance article:
Packages of commercial property loans (CMBS) are typically on short maturities and have to be refinanced every two to three years. Borrowing exploded during the pandemic when the Fed flooded the system with liquidity. That debt comes due in late 2023 and 2024.
Could the losses be as bad as the subprime crisis? Probably not. Capital Economics says the investment bubble in US residential property peaked at 6.5pc of GDP in 2007. The comparable figure for commercial property today is 2.6pc.
But the threat is not trivial either. US commercial property prices have so far fallen by just 4pc to 5pc. Capital Economics expects a peak to trough decline of 22pc. This will wreak further havoc on the loan portfolios of the regional banks that account for 70pc of all commercial property financing.
Estimates vary, but it is likely that even a 10-15 per cent increase in default rates on commercial property when the refinancing chickens come home to roost could mean about $ 100 billion in losses for banks. And these are real losses, not the notional variety sitting on the books. Will the regional banks be able to weather this? And what happens if 4-5 of them catch a cold together in this portfolio? The risk of contagion flowing up the banking food chain is real.
Lastly, the Fed, FDIC and the government took the extraordinary step of guaranteeing all deposits after the collapse of SVB to reassure depositors and not have further runs on mid-sized banks. But that didn’t stop the ever-increasing deposit erosion for FRB during April. People can do the math, and they realise there’s no way the government can fill a giant hole in case there’s a real deposit run. The FDIC, after all, has a little over $ 100 billion to act as insurance for such an eventuality. That’s loose change in the broader scheme of things. So, the depositors will flee the more you try and convince them all’s well. Plus, the blanket deposit backstop has meant there’s a moral hazard built right there for the management not to be too worried about the nature of deposits they bring or the risk of serious asset-liability mismatches.
At the time of SVB collapse, I wrote in edition # 205:
I guess one way to look at this is if you let fiscal dominance become the central canon of how you manage your economic policy, you will eventually reach the same place as other economies (mostly developing) that have indulged in the same for years. The monetary authorities in the U.S. have been accommodating the fiscal profligacy of the treasury for years. This was accentuated during the pandemic. Trillions of dollars were pumped in to save the economy. I’m not sure how much the economy needed saving then. But that bill has come now. First in the shape of inflation, followed by rapid, unprecedented rate hikes and the inevitable accidents that are showing up now. Almost certainly, a recession will follow. Isomorphic mimicry of Latin American monetary policy indeed.
Now, back to Evans-Pritchard and his article in Yahoo Finance:
The root cause of this bond and banking crisis lies in the erratic behaviour and perverse incentives created by the Fed and the US Treasury over many years, culminating in the violent lurch from ultra-easy money to ultra-tight money now underway. They first created “interest rate risk” on a galactic scale: now they are detonating the delayed timebomb of their own creation.
Chris Whalen from Institutional Risk Analyst said we should be wary of a false narrative that pins all blame on miscreant banks. “The Fed’s excessive open market intervention from 2019 through 2022 was the primary cause of the failure of First Republic as well as Silicon Valley Bank,” he said.
Mr Whalen said US banks and bond investors (i.e. pension funds and insurance companies) are “holding the bag” on $5 trillion of implicit losses left by the final blow-off phase of the Fed’s QE experiment. “Since US banks only have about $2 trillion in tangible equity capital, we have a problem,” he said.
Going back to the original question I posed - what will Fed do given these problems on hand? I guess it has decided to choose what it thinks is the least worst option. It cannot let go of its fight against inflation. It has to find a way to avoid recession. So, all it can afford is a controlled banking crisis. An oxymoron if ever there was one. But that’s where we are headed, where we will see things unfold in a slow but almost predictable manner. The Fed will try and boost the banks’ capital in the meantime and hope the best of them brave through this without any risk of contagion.
Anyway, in the worst case, there’s always Jamie Dimon and his chequebook.
Numbers that Ought to Matter: In April 2023, the Union Health Minister reported that India has 108,000 MBBS seats in 660 colleges and 118,000 BSc nursing seats in approx 900 colleges. The total number of seats on offer is quite low, despite the large number of colleges. On average, each medical college has 163 seats, and each nursing college has just 131 seats. Government policy should focus on helping existing colleges increase their intake. For more context, read edition #159.
India Policy Watch #1: Coal is Out? Naah.
Insights on issues relevant to India
— Pranay Kotasthane
Earlier this week, I came across this Business Standard report:
“India plans to stop building new coal-fired power plants, apart from those already in the pipeline, by removing a key clause from the final draft of its National Electricity Policy (NEP), in a major boost to fight climate change, sources said.”
My prior assumption was that given coal-based power’s lower costs, India would construct many more coal-powered plants over the next two decades to meet a growing economy’s demand. Hence, this news item came as a bit of a surprise. So I went through the draft National Electricity Plan to understand the reasoning.
Before we dive in, some bureaucratic knots that need untangling. The cited “final draft” of the National Electricity Policy is nowhere to be found on the Ministry of Power website. But I could find an earlier draft on the IIT Kanpur’s Centre for Energy Regulation website! A Policy document such as this only lists the priorities and steers the sector. From it arises a Plan that’s to be released every five years by the Central Electricity Authority. The Plan document is the real deal as it does demand projections through an ‘Electric Power Survey’. It then presents the energy generation mix required to meet the projected demand scenarios. A part of this elusive plan document was released, after many delays, in September 2022. Some relevant insights from the plan:
The current installed power capacity of ~400GW split looks as follows:
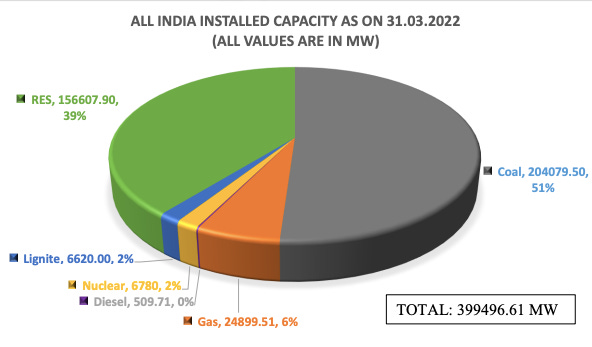
By FY32, it is projected that India’s energy demand will be 2538 Billion Units, and peak power demand will be 363 GW, up from 1624 Billion Units and peak demand of 216 GW in FY23.
Coal+Lignite accounted for 52.7% of total installed capacity in FY23.
Using a planning tool that optimises for factors such as fuel availability, operational availability, and sustainability, the Plan throws up a required power generation capacity mix.
After taking all these constraints into account, the Plan finds that by FY32, India would need an additional installed coal capacity of 42.6 GW in the base case scenario and 53.6 GW in the increased-demand scenario.
Around 25.6 GW of capacity addition is already in various stages of execution.
Now, we come to the report claiming a ban on additional coal capacity addition beyond the current in-progress projects. It essentially means that to meet the projected demand, India will have to find other sources to compensate for coal. In the best case, an additional 17 GW capacity will have to be conjured up; and in the worst-case scenario, nearly 28 GW capacity will have to be compensated. This additional capacity goes beyond the planned additions in clean energy generation. That’s why I am sceptical about this news report. It’s unlikely that government will make a blanket commitment.
If we assume the report to be true, advancing the date of halting further coal power generation will require compensation by another reliable source to provide the base load. Only two options can be imagined with today’s technology — nuclear energy and Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS).
Nuclear energy accounts for just 2 per cent of the total power generation mix today. The current plan already assumes a threefold increase in nuclear power capacity addition. For it to absorb the slack of stopping further coal addition, it has to reach six to eight times the current capacity.
Given that nuclear power generation faces the problem of high capital costs and invites protests, scaling it up is tough unless the Small Modular Reactor (SMR) technology breakthrough leads to mass adoption in India. Maybe for this reason, the government is “considering” overturning a ban on FDI in nuclear power. Expanding BESS capacity also depends on the ability to develop Lithium refining expertise and bring other options, such as Sodium-ion batteries, online.
So, stopping the building of new coal-fired power plants requires far too many other pieces of the puzzle to fall into place. Keep watching this space.
Tailpiece: check out this Puliyabaazi episode on the chemistry, geopolitics, and significance of Lithium-ion batteries.
India Policy Watch #2: Lessons from Apple’s India Journey Thus Far
Insights on issues relevant to India
— Pranay Kotasthane
Apple’s quarterly results are out. Its India revenue registered double-digit growth, prompting Tim Cook to make the now-commonplace “India is at a tipping point” statement. The last seven years have been stunning for Apple’s India business. From being shunned away by the government for their plan to import and sale of refurbished phones to becoming a poster child of electronics manufacturing in India, Apple’s India strategy has come a long way.
I’ve always wanted to know how Apple raised its India game and whether there are broader lessons for Indian public policy from this experience. So I was delighted to read Surajeet Das Gupta’s Business Standard article narrating Apple’s tryst with Indian public policy. Das Gupta identifies these milestones and speed-breakers:
In 2016, after denying the import-refurbish-sell request, Apple was told to start manufacturing in India if it wanted to set up Apple-owned retail stores.
In 2017, Apple put forward two pre-conditions for starting manufacturing in India:
“15-year duty concessions (on capital equipment, components, consumables for smartphones).. and a reduction in customs duty on completely knocked down and semi-knocked down devices to be assembled in India.”
relaxation of 30 per cent local sourcing directive for foreign direct investment (FDI) in single-brand retail stores.
After both its asks were rejected, it set up an India team to work with the government and mobile phone industry associations.
After three years of lobbying, the government relented by allowing the 30 per cent local norm to be met as an average for the first five-year period, not annually. Then the government agreed to qualify the value added by Apple’s contract manufacturers in India—regardless of the destination of these products—as “local sourcing”.
The government allowed Apple to set up an online store before the physical store if it brought over $200 million FDI and extracted a commitment that the online store couldn’t get into heavy discounting.
When PLI rules were modified to accommodate Samsung’s entry, Apple went along with the change.
After the government made the entry of FDI from China in the Indian tech sector arduous due to the Galwan clash, Apple worked with the industry body to get 12 of its Chinese suppliers approved on the condition that they would enter into joint ventures with Indian partners who would have a majority stake. (We wrote about it in edition #199).
Take a breath. And it has only been seven years. There are three ways of interpreting this journey from a public policy perspective.
First, to the extent that the government has been able to capture Apple’s China manufacturing—even if in a really small way—its approach can be called a limited success. The government can rightfully claim that Apple’s supply chain has created over a lakh jobs in India. Grabbing some part of the manufacturing of the world’s biggest company has a signalling effect as well. It will also help Apple’s Indian partners upgrade technologically and raise their standards.
Second, Apple’s up-and-down journey also serves as a warning. If the world's most well-known company had to jump as many hoops, what chance does a smaller company have? How many other businesses will have the money and patience to set up India teams that negotiate with the government to remove roadblocks, one by one, calmly? And the approval of Apple’s Chinese suppliers shows that the government is comfortable making pro-business exemptions but is uncomfortable making pro-market relaxations. There’s a risk of going overboard with the “market access in return for manufacturing” approach.
A policy analyst must also pop the opportunity cost question. Could the government have spent precious state capacity elsewhere by following a general easing of these constraints? How many companies did India lose in the process of playing hardball with Apple? And what about the Indian consumers - what did they lose as a result of these overbearing conditions? These are tough questions to answer.
Third, this journey shows that technology policy is shaping up rather well in India. Industry associations and public advocacy departments of companies are now able to put forward their demands and grouses in front of governments in a far more transparent manner. Not just that, they are able to get governments to modify policies as well.
In my view, all three interpretations are simultaneously true. But this is just the beginning of India’s electronics manufacturing journey. The steps required to strengthen it might be drastically different from the approach required to start it.
HomeWork
Reading and listening recommendations on public policy matters
[Article] Here’s a RestofWorld Q&A on the US-China chip war and its implications for India featuring one of us.
[Story] FT has an excellent visual explainer on quantum computing this week.
[Article] Niranjan Rajadhyaksha’s Mint column comparing Asian countries when their median age was 28 like India’s is today, is insightful.



